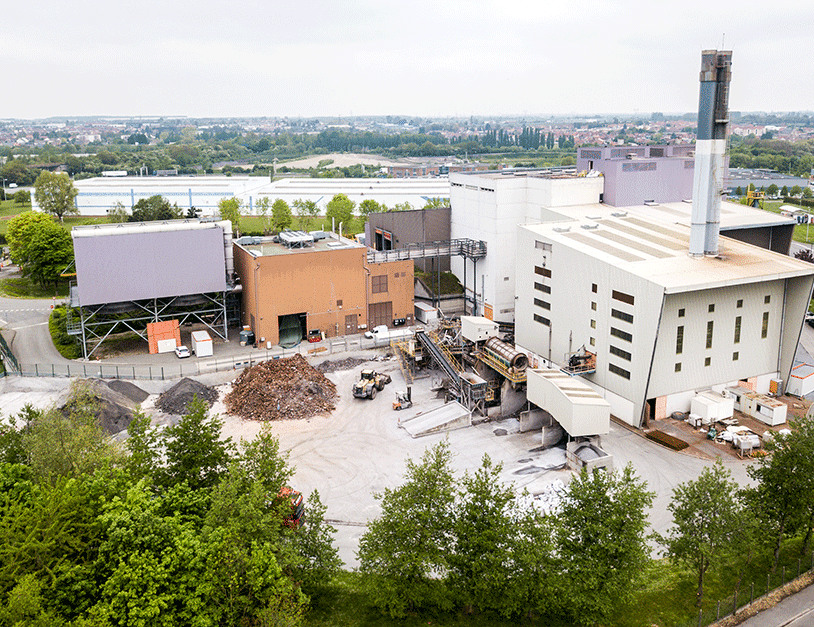
WASTE-TO-ENERGY AND BIOMASS PLANTS
At the end of the material reuse process, energy production technologies come into play. Today, they represent an extremely promising additional offer. Energy production units notably include waste-to-energy (WtE) plants, biomass plants and solid recovered fuel (SRF) plants.
WASTE FOR ENERGY PRODUCTION
Thanks to innovation and the permanent progression of technology, most waste that cannot be reused in material form, can now be used to produce energy without having a negative impact on the environment.

OUR WASTE-TO-ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Thanks to our collaboration with Altawest equipment manufacturer and its subsidiary, Inova Opérations, we operate several energy recovery sites throughout France:
4 waste-to-energy plants (WtE):
- Noyelles-sous-Lens (62)
- Pithiviers (45)
- Besançon (25)
- Chinon (37)
5 Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) plants:
- Fresnoy-Folny (76)
- Chanceaux-près-Loches (37)
- Montblanc (34)
- Bruguières (31)
THE ADVANTAGES OF OUR WASTE-TO-ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Our regional presence and logistics resources enable rapid intervention to collect and transport your waste to our energy recovery sites.
Our acquisitions and partnerships –notably Paprec Agro and Inova Opérations– enable total control over the entire energy circuit.
We are aware that energy recovery is an essential development area for the immediate future, which is why we invest in new recovery processes.


Stéphane Leterrier . Executive Director in charge of public authorities
OUR EXPERTISE AND KNOW-HOW MEAN WE CAN PROPOSE MAXIMAL RECOVERY TO OUR CUSTOMERS, EVEN FOR NON-RECYCLABLE, FINAL WASTE.

BIOMASS PLANTS
Through our subsidiaries, Paprec Agro and Inova, we have facilities to prepare the biomass used to feed wood boilers or biomass plants.
Our biomass production platforms enable different types of resources to be grouped together: class A recovered wood (untreated wood from raw wood transformation by-products, dry, untreated and unpainted wood, pallets, etc.), waste from sawmills, green waste, etc.
- This waste is sorted, shredded and mixed before being wetted to make biomass. This is then used as fuel for industrial or municipal boilers, and heating circuits.
- A biomass plant uses the combustion of waste (wood, plants, agricultural waste) to generate heat and/or electricity.
Energy is produced from the heat emitted by the combustion process, which heats the water in the boiler. The water becomes steam, which then powers the turbines and alternator of the plant to produce electricity.
Boiler systems that produce both heat and electricity are described as cogeneration systems.
SRF PLANTS
Solid recovered fuel (SRF) is produced from waste that cannot be sorted or recycled. This waste is known as non-recyclable waste. It can be wood, plastic, paper, cardboard from ordinary industrial waste, construction site waste or bulk waste from recycling centres.
SRF production can process up to 98% of non-recyclable waste.
also discover





